Air Quality Monitoring Technical Note – membraPure IONUS Ion Chromatograph
Optimal air quality is essential for both human health and a well-functioning environment. Ensuring safe and healthy air, particularly in occupational settings, requires robust and reliable monitoring strategies.
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), and theKorea Occupational Safety and Health Agency (KOSHA) have published methods for sampling and testing air in occupational settings.
A number of these published methods recommend Ion Chromatography (IC) as the analytical technique to use to properly identify and quantify the ionic contaminants in these settings. The IC technique offers high sensitivity, selectivity, and the ability to analyze multiple ionic species, making it particularly well-suited for determining a wide range of air pollutants.
At membraPure, we explored the methods published by NIOSH, OSHA, and KOSHA recommending Ion Chromatography as the preferred analytical technique for the air monitoring procedures listed below.
Our goal was to confirm the capability of our IONUS Ion Chromatograph to perform these applications equal to or better than the method prescribed in the methods. Several of these methods were published more than 30 years ago. IC systems, IC columns, and software for instrument control and data reporting have changed significantly, although several of the methods do not reflect these improvements.
Our team at membraPure GmbH reviewed the methods and outlined appropriate testing protocols to perform the separations indicated within the methods, although we did not actually perform the air scrubbing or sample collection techniques. We prepared standards in ultra pure water to simulate the sample as if collected by air scrubbing techniques as stated in the methods.
Our goal was to demonstrate the IONUS Ion Chromatograph has the ability to perform the various NIOSH, OSHA, and KOSHA methods as listed in the table Table 1& Table 2 below to produce the highest quality result at an affordable cost of ownership.
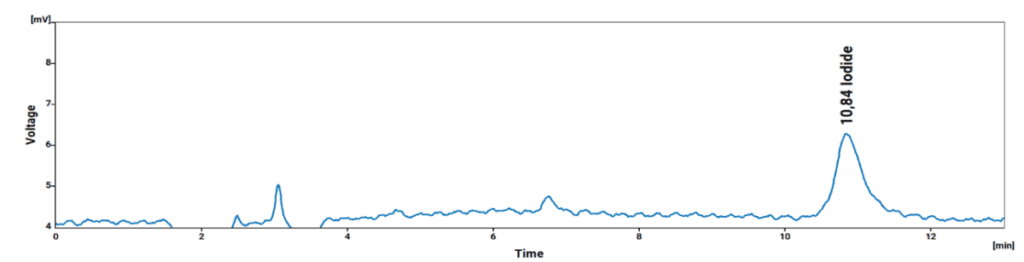
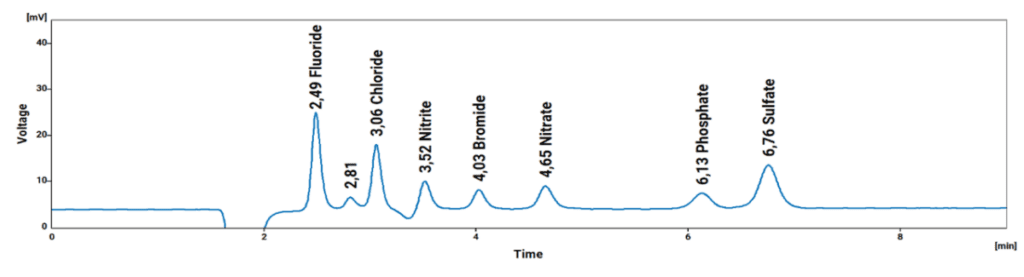
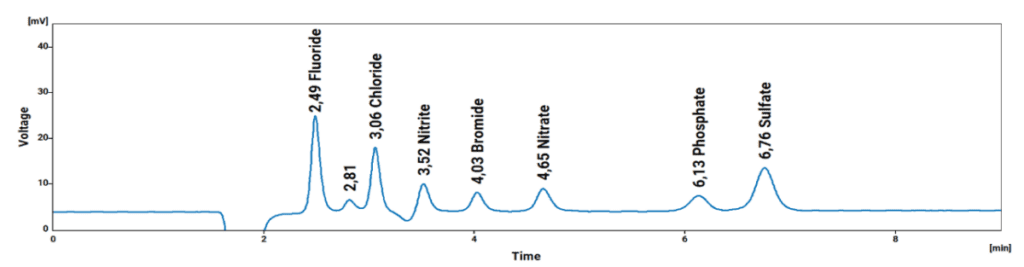
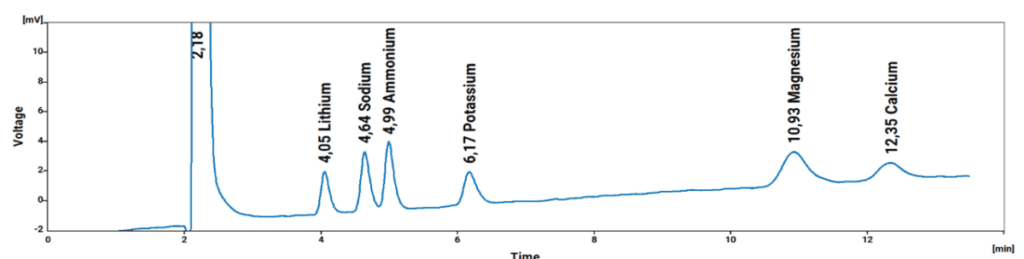
The IONUS Ion Chromatograph is a robust system ideally suited for the analysis of the prescribed Anions, Cations, Formic Acid, and Iodide as shown in the chromatograms (Fig. 1 to Fig. 4) below.
When an application change is required on the IONUS, such as when changing from Anions to Cations, the switchover is simple with minimal time required. We were able to demonstrate a change from Anions to Cations in under 20 minutes with a stable baseline.
We were also able to demonstrate most of the anions can be performed without a column or eluent change, improving speed between analyte detection.
Operating Cation Conditions of the Method
| IC System | IONUS Ion Chromatograph |
| Column | Repromer CAT, 7 µm, 4 x 250 mm |
| Eluent | 4 mM Nitric Acid |
| Flow | 0.7 mL/ min |
| Temperature | 35 °C |
| Loop | 50 µL |
| Water Source | Aquinity² P10 Analytical (0.055 µS/cm, Type I) |
Operating Anion Conditions of the Method
| IC System | IONUS Ion Chromatograph |
| Column | ICSep AN2 Analytical 4 x 250 mm |
| Eluent | 3.5 mM Carbonate / 1.0 mM Bicarbonate / 0.05 mM Sodium Thiocyanate |
| Flow | 1.0 mL/min |
| Temperature | 35 °C |
| Suppressor | membraPure IC Suppressor² |
| Regenerant | 1 N Sulfuric Acid |
| Sample | Dilution and filtration with IC syringe filters |
| Loop | 50 µL |
| Water Source | Aquinity² P10 Analytical (0.055 µS/cm, Type I) |
Other Methods for Air Monitoring Using IC:
Method 26 and 26A using IONUS:
Ion chromatography (IC) plays a critical role in the accurate measurement of various air pollutants from stationary sources, including sulfur dioxide (SO2) and halides, as exemplified by EPA Methods 26 and 26A.
These methods, widely used for compliance testing, rely on IC for the precise quantification of these target analytes.
Both methods typically involve isokinetic sampling to ensure representative sample collection, followed by absorption of the pollutants into an impinger solution.
For SO2 analysis, the collected SO2 is oxidized to sulfate before IC analysis. When used for halides, the specific sample preparation and analytical procedures may vary.
While similar in their core principles, Methods 26 and 26A often incorporate modifications to the sampling or analytical procedures to address specific challenges or improve performance for different analytes.
For instance, Method 26A frequently includes a heated filter to remove particulate matter prior to SO2 absorption, minimizing potential interferences.
The membraPure IONUS Ion Chromatograph is well-suited for performing these essential EPA methods, including both SO2 and halide analyses. Its robust design and advanced analytical capabilities make it a reliable platform for measuring emissions in compliance with regulatory requirements.
The IONUS offers the high sensitivity and selectivity necessary to accurately quantify sulfate and various halide ions, even in complex emission matrices.
Furthermore, its automated features and user-friendly interface streamline the analytical process, enhancing laboratory efficiency and productivity.
By utilizing the IONUS, laboratories can confidently perform EPA Methods 26 and 26A for a range of pollutants, ensuring accurate emission monitoring and contributing to environmental compliance efforts. We will explore the use of the IONUS for Method 26 and 26A in a future application note.
ASTM D7614-20 using IONUS PCD:
ASTM D7614-20 outlines a method for determining hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) in ambient air using ion chromatography (IC) with post-column derivatization and UV-Vis detection.
This standard method is crucial for accurate monitoring of Cr(VI), a known carcinogen, in air samples. The method involves collecting airborne particulate matter on a filter, followed by extraction of the Cr(VI) species.
The extract is then analyzed by IC, where Cr(VI) is separated from other chromium species and subsequently derivatized post-column to form a colored complex that is detected by a UV-Vis detector. This approach provides both selectivity and sensitivity for Cr(VI) quantification, essential for ensuring compliance with air quality regulations and protecting public health.
The membraPure IONUS PCD Ion Chromatograph is ideally suited for performing analyses according to ASTM D7614-20. Its robust design and advanced separation capabilities ensure accurate and reliable quantitation of Cr(VI) in air samples. We will explore in more detail the IONUS PCD for the determination of Hexavalent Chromium in a future application note.
Figure 1: Ion Chromatograph IONUS (PCD)
Conclusion
In summary, the membraPure IONUS Ion Chromatograph stands as a robust and versatile solution for modern air monitoring laboratories.
Its affordability, sensitivity, reproducibility, and robust design make it an ideal platform for the accurate determination of anions, cations, formate, and iodide, directly addressing the analytical requirements of the methods discussed.
The IONUS excels in meeting both TWA* (Time-Weighted Average) and STEL* (Short-Term Exposure Limit) reporting capabilities, ensuring compliance with air quality regulations, and providing the confidence laboratories need to generate reliable data.
TWA is the average concentration of a substance in air over a specified period, such as an 8-hour workday. It reflects the cumulative exposure an individual can safely experience without adverse health effects over time. The purpose of TWA limits is protect individuals against chronic or long-term health risks from sustained low-level exposure.
STEL is the maximum concentration of a substance allowed over a short period, typically 15 minutes, that workers can be exposed to without acute effects. It’s a ceiling limit for brief, intense exposure. The purpose of STEL limits is to protect individuals against immediate or acute health effects that could occur from spikes in concentrations, even if below TWA limits.
Beyond just meeting current needs, the IONUS streamlines workflows, minimizes downtime, and empowers lab personnel to focus on other critical tasks, boosting overall productivity and contributing to more effective air quality management.
From routine compliance measurements to specialized research investigations, the IONUS offers a comprehensive and future-proof solution.
By choosing the IONUS, laboratories gain a high-quality analytical instrument and invest in a system that improves efficiency, reduces costs, and ultimately contributes to a healthier environment.
The IONUS represents a significant advancement in air monitoring technology, providing a reliable and cost-effective way to ensure accurate air quality assessments and protect public health.
Table 1: List of Analytes and Methods
| Analyte | Form | Instrument | KOSHA | NIOSH | OSHA |
| Ammonia | NH4 | IC-CDD | A-176-2019 | 6016 | ID-188 |
| Hydrogen Fluoride | HF | IC-CDD | A-154-2018 | 7906 | |
| Hydrogen Bromide | HBr | IC-CDD | A-155-2018 | 7907 | |
| Hydrogen Chloride | HCl | IC-CDD | A-183-2020 | 7907 | ID-174SG |
| Nitric Acid | HNO3 | IC-CDD | A-185-2020 | 7907 | IC-165SG |
| Phosphoric Acid | H3PO4 | IC-CDD | A-184-2020 | 7908 | ID-111 |
| Sulfuric Acid | H2SO4 | IC-CDD | A-179-2019 | 7908 | ID-113 |
| Fluorine | F | IC-CDD | 7906* | ID-110 (ISE) | |
| Formic Acid | HCOOH | IC-CDD | 2011 | ||
| Iodine | I | IC-CDD | A-46-2021 | 6005 | ID-212 |
| Sulfur Dioxide | SO2 | IC-CDD | 6004 | ||
| Hydrogen Sulfide | H2S as Sulfate | IC-CDD | 6013 | ||
| Ozone | O3as Nitrate | IC-CDD | ID-214 | ||
| Chlorine | Cl | IC-CDD | 6011 | ||
| Bromine | Br | IC-CDD | 6011 | ||
| Nitrogen Monoxide | NO | IC-CDD | 6014 | ID-190 | |
| Nitrogen Dioxide | NO2 | IC-CDD | 6014 | ID-182 |
Note: * NIOSH Method 7906 analyzes Fluoride by IC. OSHA ID-110 is an ISE method.
Table 2: Analyte Concentration Range
| Analyte | Form | IC Calibration Range, ppm* | KOSHA | NIOSH | OSHA |
| Ammonia | Ammonium | 1 – 20 | A-176-2019 | 6016 | ID-188 |
| Hydrogen Fluoride (Aerosol and Gas) | Fluoride | 0.01 – 0.25 Gas 0.3 – 10 Particulate | A-154-2018 | 7906 | |
| Hydrogen Bromide | Bromide | 0.4 – 4 | A-155-2018 | 7907 | |
| Hydrogen Chloride | Chloride | 0.4 – 4 | A-183-2020 | 7907 | ID-174SG |
| Nitric Acid | Nitrate | 0.4 – 4 | A-185-2020 | 7907 | IC-165SG |
| Phosphoric Acid | Phosphate | 0.8 – 8 | A-184-2020 | 7908 | ID-111 |
| Sulfuric Acid | Sulfate | 0.2 – 8 | A-179-2019 | 7908 | ID-113 |
| Fluorine | Fluoride | 0.003 – 0.008 | 7906 ** | ID-110 (ISE) | |
| Formic Acid | Formate | 0.13 – 12 | 2011 | ||
| Iodine | Iodide | 0.05 – 5 | A-46-2021 | 6005 | ID-212 |
| Sulfur Dioxide | Sulfate | 0.2 – 8 | 6004 | ||
| Hydrogen Sulfide | Sulfate | 0.6 – 14 | 6013 | ||
| Ozone | Nitrate | 0.5 – 10 | ID-214 | ||
| Chlorine | Chloride | 0.007 – 0.5 | 6011 | ||
| Bromine | Bromide | 0.008 – 0.4 | 6011 | ||
| Nitrogen Monoxide | Nitrite | 0.5 – 50 | 6014 | ID-190 | |
| Nitrogen Dioxide | Nitrite | 0.5 – 20 | 6014 | ID-182 |
Note: * The Range listed for each method was extracted from the method #‘s list and reported in this table.
Note: ** NIOSH Method 7906 analyzes Fluoride by IC. OSHA ID-110 is an ISE method.
Chromatograms: