Amino acids Tyrosine and Phenylalanine as biomarkers for Phenylketonuria analyzed by ARACUS
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a genetic metabolic disease. It is caused by decrease of the activity of phenylalanine hydroxylase in body or lack of its coenzyme tetrahydrobiopterin, which leads to hindered metabolism of phenylalanine to tyrosine, increase of concentration of phenylalanine in blood and tissues, significant increase of phenylpyruvate, phenylacetic acid and phenyllactic acid in urine. So it is called “phenylketonuria”. Phenylalanine is an essential amino acid for human’s growth and metabolism. Part of phenylalanine from food is used for protein synthesis, another part is converted into tyrosine by the action of phenylalanine hydroxylase to function.
Symptoms of Phenylketonuria
Most children with PKU behave normally at birth. There is no obvious special clinical symptom during neonatal period. Untreated children gradually show mental retardation and motor development after 3 to 4 months, their hair turns from black to yellow, skin becomes white, whole body and urine have a special rat smell, often have eczema. With growing up, their mental retardation becomes more and more obvious, about 60% of older children have severe intellectual disabilities. Most of those who receive treatment within one month after birth do not have intellectual impairment. The later the treatment, the more obvious the brain damage.
Diagnosis of Phenylketonuria
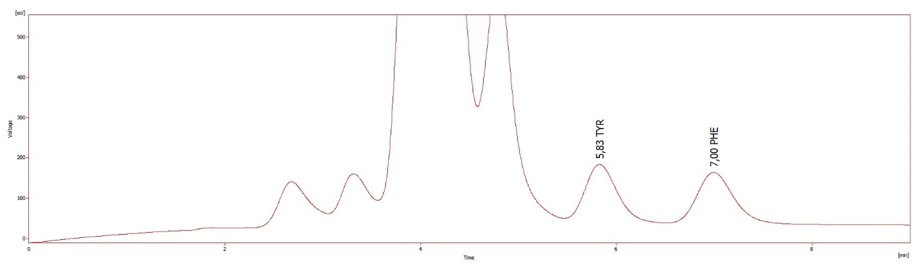
Since phenylketonuria first manifests as an increase of the concentration of phenylalanine in the blood, measure the concentration of phenylalanine in the blood is the preferred method for diagnosing PKU. Generally, the blood phenylalanine is 3120mmol/L, which is judged to be positive. For further diagnosis, if the blood tyrosine concentration can be detected at the same time, it is better to analyze the ratio of phenylalanine to tyrosine, and 3/2 is judged as positive.
Treatment to classic PKU, moderate hyperphenylalanineemia, and moderate to mild hyperphenylalaninemia
These three types are caused by abnormalities in phenylalanine hydroxylase itself, but there is no phenylalanine, the drug of amino acid hydroxylase, the only way to reduce the intake of phenylalanine from food is to control the concentration of phenylalanine in the body at an appropriate level.
Since ordinary foods, especially foods containing high level of protein, such as meat, fish, shrimp, eggs and soy products, contain high levels of phenylalanine, it is necessary to reduce the intake of these kinds of food and supply them with phenylalanine acidic-free formula milk or protein powder to provide other essential amino acids for the body. But phenylalanine is one of the essential amino acids of the human body and must meet its growth and development needs. Too low phenylalanine in the body can also cause diseases. Therefore, those children need to eat “special medical food.”
Neonatal screening in China has been fully implemented since 1985. There are three main types of screening and treatment. The current screening coverage rate is still low. The incidence of PKU (Phenylketonuria) and CH (Congenital Hypothyroidism) were investigated. All screened subjects were subject to acupuncture at the heel 72 hours after birth.
Comparing to traditional MS method, amino acid analysis method can identify more kinds of amino acids to solve the disadvantage that some amino acids with the same or similar mass spectra cannot be distinguished by MS method: for example, the following amino acids have the same or similar Mass spectrometry.
– Leucine (131 17 g/mol)
– Isoleucine (131 17 g/mol)
– Allo-isoleucine (131 17 g/mol)
– Hydroxyproline (131 13 g/mol)
Allo-isoleucine in blood or urine is a significant marker of maple syrup uria disease (MSUD).
The advantages of amino acid analysis method include higher accuracy, simple operation, better reproducibility and accuracy. Accuracy is very important for monitoring the health status of patients with metabolic disorders. Accurate measurement of amino acid concentration in blood samples is an important basis for optimizing treatment, care and dietary conditioning of patients. Through active treatment, care and dietary conditioning, the health of patients with amino acid metabolism disorders can be guaranteed.