Type determination of amino acid based plant fertilizer with post column derivatization with Amino Acid Analyzer ARACUS
Amino acid water-soluble plant fertilizer is a new type of functional fertilizer, which can be quickly absorbed by plants. It has characteristics of increasing yield, improving fruit quality, stress resistance, improving soil and improving drug utilization. This kind of plant fertilizer plays a positive role in solving problems such as soil quality decline, environmental pollution and pesticide residues.
Recent studies have confirmed that amino acid-based fertilizers can enhance plant metabolic activity by improving nitrogen assimilation and stimulating key enzymes like nitrate reductase and glutamine synthetase (Khan et al., 2019).
With the deepening of people’s awareness of ecological and environmental protection, more and more attentions have been paid to the research and application on amino acid water-soluble fertilizer. Rational use of amino acid water-soluble plant fertilizers can improve crop utilization efficiency of natural resources. It is a relatively safe way to reduce investment and increase efficiency.
Additionally, amino acid-based fertilizers have been linked to improvements in plant stress tolerance, such as enhanced drought and salinity resistance, due to their role in osmotic regulation and antioxidant activity (Colla et al., 2017).
According to appearance of amino acid water-soluble plant fertilizers, it can be divided into liquid and solid; According to type, it can be divided into two types, medium element type and trace element type. According to the stipulation of the technical standard of the Ministry of Agriculture “NY 1429-2010”, the content of free amino acids in solid and liquid products of amino acid water-soluble fertilizers cannot be less than 10.0% and 100 g/L respectively.
These concentration thresholds are set to ensure optimal biological efficacy and compatibility with plant physiology, as low amino acid levels could result in suboptimal absorption and reduced biostimulant activity (Saa et al., 2015).
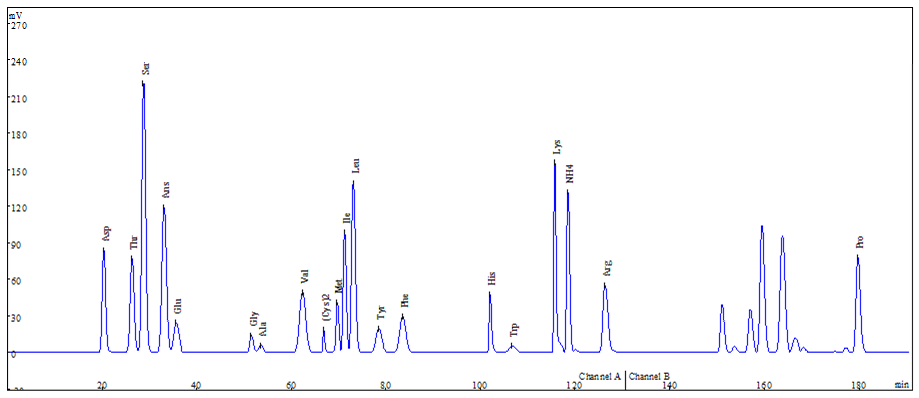
Because of the complexity of sample matrix, the pretreatment to analyzing free amino acids in water-soluble fertilizers is very important. Please refer to the standard “NY 1429-2010” to prepare sample, then use Amino Acid Analyzer to analyze content of amino acids in the sample.
Post-column derivatization methods, such as ninhydrin or o-phthalaldehyde (OPA) reactions, are widely used for accurate quantification of amino acids due to their sensitivity and reliability in complex matrices (Cohen & Michaud, 1993).
Moreover, the use of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled with amino acid analysis allows for precise profiling, which is essential for the formulation quality and regulatory compliance of fertilizers (Rosa et al., 2019).
References:
- Khan W, Rayirath UP, Subramanian S, et al. “Seaweed extracts as biostimulants of plant growth and development.” J Plant Growth Regul. 2009;28(4):386–399. doi:10.1007/s00344-009-9103-x
- Colla G, Rouphael Y, Canaguier R, Svecova E, Cardarelli M. “Biostimulant action of a plant-derived protein hydrolysate produced through enzymatic hydrolysis.” Front Plant Sci. 2017;8:2202. doi:10.3389/fpls.2017.02202
- Saa S, Olivos-Del Rio A, Castro S, Brown PH. “Amino acid–chelates in plant nutrition.” Front Plant Sci. 2015;6:696. doi:10.3389/fpls.2015.00696
- Cohen SA, Michaud DP. “Synthesis of a fluorescent derivatizing reagent, 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate, and its application for the analysis of hydrolysate amino acids via high-performance liquid chromatography.” Anal Biochem. 1993;211(2):279-287. doi:10.1006/abio.1993.1270
- Rosa M, Prado C, Podazza G, et al. “Amino acids in plants: regulation and functions during development and stress.” Plant Biol. 2019;21(S1):203-220. doi:10.1111/plb.12865

