Quality assurance of the composition of amino acid containing therapeutics with Amino Acid Analyzer ARACUS
It is well known, there are 20 kinds of amino acids which comprise the protein of human. According to perspective of nutrition, instead of coming from food, the amino acids which can be synthesized in human body are called non-essential amino acids; the amino acids, which cannot be synthesize in human body or its synthesis speed is much lower than the speed of its consumption, must be supplied by food protein, are called essential amino acids.
Amino acid imbalance or deficiency is linked to impaired protein synthesis, immune dysfunction, and delayed recovery in clinical settings, highlighting the importance of precise amino acid formulations in medical nutrition (Wu, 2013).
Essential amino acids
There are 8 kinds of essential amino acids, whose functions are as follows:
- Methionine: comprising hemoglobin, tissue and serum, enhance the physiological functions of the spleen, pancreas and lymph
- Lysine: promotes brain’s growth, component of liver and gallbladder, promote fat metabolism
- Tryptophan: promote generation of gastric juice and pancreatic juice
- Phenylalanine: participate in eliminating loss of kidney and bladder function
- Threonine: has the function of transforming some amino acids to their balance
- Isoleucine: Participate in the regulation and metabolism of the thymus, spleen and lower brain glands
- Leucine: balance isoleucine
- Valine: acts on the corpus luteum, breast and ovary
Additionally, branched-chain amino acids (leucine, isoleucine, and valine) are particularly important for muscle protein synthesis and are frequently used in therapeutic interventions for sarcopenia, liver disease, and critical illness (Shimomura et al., 2006).
Amino acid injections in medicine
For patients who are unable to eat normally, chronically malnourished, cachexia, and critically ill, and cannot take in the essential amino acids for human body like normal people. They need parenteral nutrition to maintain the basic nutritional status of patients, promote wound healing and disease recovery. So amino acid injection was produced. Generally, amino acids injections are classified into balance compound type and therapeutic compound type.
Clinical studies show that amino acid infusions significantly reduce the risk of nitrogen loss, enhance immune function, and improve patient outcomes, particularly in intensive care and surgical settings (Casaer et al., 2011).
Balance compound amino acids:
Used for supplement of nutrition. Normally are composed of more than 14 amino acids, in which, the ratio of non-essential amino acids to essential amino acids is close to 1. The 18 AA preparations used for supplement of nutrition includes 18AA-I, 18AA-II, 18AA-III and 18AA-IV etc.
Such balanced formulas are essential to ensure sufficient substrate availability for protein synthesis and maintenance of metabolic homeostasis (Riedel et al., 2020).
Therapeutic compound amino acids:
Used for diseases, whose ratio of non-essential amino acids to essential amino acids is designed according to the characteristics of diseases. Generally, divided into: 9AA; 6AA; 18AA-VIII; Alanyl Glutamine Injection, etc.
Tailored amino acid formulations are particularly important in specific clinical conditions, such as hepatic encephalopathy, where branched-chain amino acids are favored to reduce ammonia levels and support neurological recovery (Muto et al., 2006).
Under the condition of sufficient energy supply, amino acid injection is able to enter tissue cells, participate in the synthesis and metabolism of protein, obtain the nitrogen balance, and generate enzymes, hormones, antibodies, structural proteins and other physiologically active substances, which promote tissue healing and restore normal physiology Features.
Furthermore, glutamine-containing preparations are often used to promote gut barrier function and modulate inflammation in critically ill patients (Wischmeyer et al., 2014).
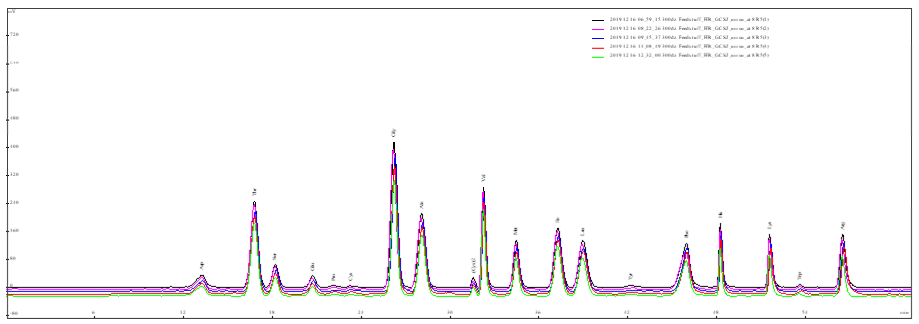
Amino acid injection contains the essential amino acids for human body. According to requirements, the content of its components can be analyzed by an amino acid analyzer, which can accurately obtain the content of each component and make its due contribution to medicine research and development.
High-performance amino acid analyzers, employing post-column derivatization with ninhydrin or OPA, are widely used in pharmaceutical quality control to ensure batch-to-batch consistency and regulatory compliance (Rogers et al., 2020).
References:
- Wu G. “Functional amino acids in growth, reproduction, and health.” Adv Nutr. 2013;4(6):658-665. doi:10.3945/an.113.004655
- Shimomura Y, Yamamoto Y, Bajotto G, et al. “Nutraceutical effects of branched-chain amino acids on skeletal muscle.” J Nutr. 2006;136(2):529S-532S. doi:10.1093/jn/136.2.529S
- Casaer MP, et al. “Early versus late parenteral nutrition in critically ill adults.” N Engl J Med. 2011;365(6):506-517. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1102662
- Riedel S, et al. “The role of balanced amino acid solutions in clinical nutrition.” Clin Nutr. 2020;39(10):3011-3017. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2020.01.008
- Muto Y, Sato S, Watanabe A, et al. “Effects of oral branched-chain amino acid granules on event-free survival in patients with liver cirrhosis.” Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;3(7):705-713. doi:10.1016/S1542-3565(05)00141-6
- Wischmeyer PE, et al. “Glutamine supplementation in clinical nutrition.” Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2014;17(2):164-170. doi:10.1097/MCO.0000000000000031
- Rogers S, et al. “Advances in post-column derivatization techniques for amino acid analysis.” J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2020;1155:122295. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2020.122295

