Technischer Hinweis – Nachweisgrenzen – Kationen – IONUS Ionenchromatograph
Das membraPURE IONUS-Team wollte eine technische Notiz über die Fähigkeiten des IONUS für Kationen erstellen. Dabei haben wir die Nachweisgrenzen unter Verwendung einer neuen 4mm x 250mm Kationensäule validiert. Die Nachweisgrenzen für ein- und zweiwertige Kationen sind in Tabelle 2 (ICH) und Tabelle 3a und 3b (DIN) aufgeführt. Die Nachweisgrenzen wurden auf der Grundlage der Datensätze berechnet, wobei die Nachweisgrenzen nach zwei Methoden berechnet wurden: ICH-Richtlinien und DIN 32645.
a) Die Daten wurden nach den ICH-Leitlinien berechnet, die für die Leitlinie zur Validierung von Analyseverfahren verwendet werden.
b) Die Daten wurden nach der Norm DIN 32645 berechnet, die in der chemischen Analytik zur Bestimmung der Nachweis-, Identifizierungs- und Quantifizierungsgrenzen unter wiederholbaren Bedingungen angewendet wird.
In Gesprächen mit Kunden fiel uns auf, dass ausschließlich von LOD oder LOQ in pmol gesprochen wurde, ohne dass ein Bezug zur Konzentration oder zu den Parametern des Versuchsaufbaus hergestellt wurde. Bei den Konzentrationswerten, die nach der von uns in der Vergangenheit bevorzugten, im deutschen und europäischen Raum bekannten, international aber relativ unbekannten Methode DIN 32645 ermittelt wurden, stießen wir meist auf wenig Verständnis.
Demgegenüber scheint die ICH-Methode einen breiteren Bekanntheitsgrad zu haben, wie wir mit anderen Geschäftspartnern diskutiert haben.
Wir haben uns daher entschlossen, die Werte nach zwei Methoden zu berechnen und dem Kunden die Wahl zu lassen, welchen Daten er folgen möchte. Bei der DIN-Methode haben wir uns für zwei unterschiedliche Ermittlungsmethoden entschieden, um die Untersuchungen vollständig abbilden zu können. Nachfolgend finden Sie in Tabelle 1 eine übersichtliche Gegenüberstellung der beiden Methoden.
Auf Wunsch können wir die Rohdaten zur Verfügung stellen, so dass der Kunde seine eigenen Berechnungen durchführen kann.
Bedingungen für die Anwendung der Methode:
| IC System | IONUS Ion Chromatograph |
| Säule | Repromer CAT, 7 mm, 4 mm x 250 mm |
| Eluent | 4.0 mM Nitric Acid |
| Eluent Flussrate: | 0.7 mL/min |
| Temperatur der Säule | 40°C |
| Injektion | 20 µL |
| Wasserquelle | Aquinity² P10 Analytical (0.055 µS/cm, Type I) |
Vorbereitung der Proben
Wir verwendeten 1000 ppm-Standards (Inorganic Ventures), die vom Lieferanten zertifiziert sind und auf Natrium basieren.
Unter Verwendung der vorbereiteten individuellen 1000 mg/Kg-Standards wurde ein gemischter Arbeitsstandard auf Vorrat hergestellt. Mit dem Stammstandard wurden verschiedene Konzentrationsbereiche nach Gewicht erstellt, um die Kalibrierkurve für das Projekt zu entwickeln. Die genauen Massenwerte, die in den Arbeitsblättern des Labors aufgezeichnet wurden, können auf Anfrage zur Verfügung gestellt werden.
Tabelle 1: Vergleich zwischen den Berechnungen der LOD nach ICH und DIN 32645
| Scope | ICH Q2(R1) | DIN 32645 |
| Objective | Validation of analytical methods in the pharmaceutical sector. | Definition and determination of detection, quantification, and determination limits in chemical analysis. |
| Definition of LOD | Smallest amount of an analyte that can be detected with acceptable certainty. | Smallest concentration of an analyte distinguishable from the blank value with a predefined statistical confidence. |
| Calculation Method | LOD = 3.3 × (σ/S), where σ is the standard deviation of the signal, and S is the slope of the calibration curve. | Uses the standard deviation of the blank value or the residuals from the calibration curve to calculate the detection limit. |
| Required Data | Multiple measurements of low-concentration samples to determine σ; calibration curve to determine S. | Measurements of blank samples and/or calibration standards; statistical evaluation to determine standard deviations and calibration function. |
| Scope of Application | Pharmaceutical analysis, particularly for validating quality control methods for drugs. | General chemical analysis, including environmental analysis and other fields requiring detection and quantification limits. |
| Statistical Basis | Based on the standard deviation of the signal and slope of the calibration curve; considers method precision. | Detailed statistical methods to determine detection, quantification, and determination limits; accounts for both systematic and random errors. |
| Practical Implementation | Requires creating a calibration curve in the low-concentration range and performing multiple measurements to calculate the standard deviation. | Involves detailed statistical tests, including variance homogeneity, linearity checks, and outlier detection. |
| Advantages | Relatively simple calculation; widely used in the pharmaceutical industry; tailored to drug analysis requirements. | Comprehensive and detailed methodology; applicable to a wide range of analytical procedures; provides clear definitions and statistical reliability. |
| Disadvantages | May lack detailed statistical assurance; designed specifically for pharmaceutical applications and may not directly apply to other fields. | More complex statistical requirements; requires extensive data collection and analysis; potentially more labor-intensive to implement. |
Um alle Partikel zu entfernen, wurden die vorbereiteten Lösungen durch einen Ionenchromatographie-Filter (IC-Filter) mit einer Porengröße von 0,22 µm filtriert. Die gefilterten Lösungen wurden dann zur Lagerung und anschließenden Analyse in 1,5-mL-Fläschchen umgefüllt, die mit Septakappen verschlossen waren.
Um die Zuverlässigkeit der Daten zu gewährleisten und experimentelle Fehler zu minimieren, wurden für jede Probenlösung 10-15 Wiederholungsinjektionen durchgeführt. Zusätzlich wurden 10-20 Injektionen von Leerproben, die nur UPW enthielten, durchgeführt. Diese Leerwertinjektionen dienen dazu, ein stabiles Basissignal zu ermitteln und mögliche Verunreinigungen innerhalb des Analysesystems zu identifizieren. Die erfassten chromatographischen Daten wurden mit der Clarity-Software (DataApex) verarbeitet und analysiert. Die Endergebnisse wurden dann ausgewertet und mit den etablierten Analysestandards oder den einschlägigen gesetzlichen Normen verglichen.
Berechnungen:
Nachfolgend finden Sie eine Zusammenfassung der Datenauswertungen und der Bestimmung der Nachweisgrenzen in Form von Aufzählungspunkten:
ICH-Methode [1]:
- Bestimmen des durchschnittlichen Signals (Peakfläche) für jede Konzentrationsstufe
- Berechnen einer linearen Regression des Signals als Funktion der Konzentration
- Bestimmen der Standardabweichung der Kalibrierkurve.
- Anwendung der Formeln (1), (2) und (3) zur Berechnung von LOD, LOI bzw. LOQ.

DIN 32645 Blank Methode [2]:
- Bestimmen Sie das durchschnittliche Signal (Peakfläche) für jede Konzentrationsstufe
- Berechnen Sie eine lineare Regression des Signals als Funktion der Konzentration
- Berechnen des mittleren Signals (Rauschens) und der Standardabweichung der Blindproben.
- Bestimmen Sie die t-Student-Rechnung für ein System mit x Freiheitsgraden (y Anzahl der Leerwertmessungen) und einem angestrebten Konfidenzintervall von 95%.
- Berechnen Sie das kritische Signal, Gleichung (4)
y_k=y ̅_L+t∙σ_L (4)
Wenden Sie die Formeln (5), (6) und (7) an, um die LOD, LOI bzw. LOQ zu berechnen.
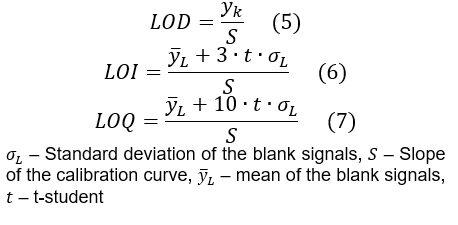
DIN 32645 Kalibrierkurvenmethode [2]:
- Bestimmen Sie das durchschnittliche Signal (Peakfläche) für jede Konzentrationsstufe
- Berechnen Sie eine lineare Regression des Signals als Funktion der Konzentration
- Bestimmen Sie die Standardabweichung der Kalibrierkurve.
- Bestimmen Sie den t-Student-Wert. Für ein System mit 9 Freiheitsgraden (11 Konzentrationsstufen) und einem angestrebten Konfidenzintervall von 95% beträgt der t-student-Wert 1,833113.
- Wenden Sie die Formeln (8), (9) und (10) an, um die LOD, LOI bzw. LOQ zu berechnen.

Ergebnisse
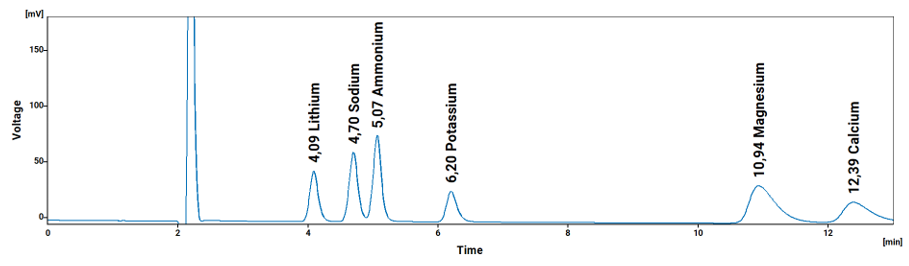
Tabelle 2: Ungefähre Nachweisgrenzen für Kationen in Reagenzwasser für ein einzelnes Labor gemäß der ICH-Methode
| Analyte / Peak # | Symbol | Retention Time / min | LOD / ppm | LOI /ppm | LOQ / ppm |
| Lithium / 1 | Li | 4.07 | 0.019 | 0.028 | 0.056 |
| Sodium / 2 | Na | 4.66 | 0.078 | 0.118 | 0.235 |
| Ammonium / 3 | NH3 | 5.02 | 0.092 | 0.139 | 0.278 |
| Potassium / 4 | K | 6.18 | 0.264 | 0.399 | 0.799 |
| Magnesium / 5 | Mg | 10.93 | 0.075 | 0.114 | 0.228 |
| Calcium / 6 | Ca | 12.35 | 0.184 | 0.279 | 0.559 |
Tabelle 3a: Ungefähre Nachweisgrenzen für Einzel-Labor-Kationen in Reagenzwasser nach DIN 32645 Blanko-Methode
| Analyte / Peak # | Symbol | Retention Time / min | LOD / ppm | LOI /ppm | LOQ / ppm |
| Lithium / 1 | Li | 4.07 | 0.005 | 0.010 | 0.028 |
| Sodium / 2 | Na | 4.66 | 0.017 | 0.035 | 0.099 |
| Ammonium / 3 | NH3 | 5.02 | 0.014 | 0.030 | 0.084 |
| Potassium / 4 | K | 6.18 | 0.032 | 0.067 | 0.190 |
| Magnesium / 5 | Mg | 10.93 | 0.010 | 0.022 | 0.062 |
| Calcium / 6 | Ca | 12.35 | 0.019 | 0.039 | 0.111 |
Tabelle 3b: Ungefähre Nachweisgrenzen für Einzel-Laboratorien für Kationen in Reagenzwasser, gemäß DIN 32645 Kalibrierkurvenmethode
| Analyte / Peak # | Symbol | Retention Time / min | LOD / ppm | LOI /ppm | LOQ / ppm |
| Lithium / 1 | Li | 4.07 | 0.010 | 0.031 | 0.103 |
| Sodium / 2 | Na | 4.66 | 0.043 | 0.129 | 0.431 |
| Ammonium / 3 | NH3 | 5.02 | 0.051 | 0.153 | 0.509 |
| Potassium / 4 | K | 6.18 | 0.146 | 0.439 | 1.465 |
| Magnesium / 5 | Mg | 10.93 | 0.042 | 0.125 | 0.417 |
| Calcium / 6 | Ca | 12.35 | 0.102 | 0.307 | 1.024 |
Schlussfolgerungen
Nach dem Vergleich von Chromatographiesäulen verschiedener Hersteller wurde die Repromer CAT-Säule als die am besten geeignete Säule in Bezug auf das Preis-Leistungs-Verhältnis identifiziert. In Anbetracht der Tatsache, dass nur das untere Injektionsvolumen gewählt wurde und auch Injektionsvolumina von 50 oder 100 µL möglich sind, zeigt das System, dass es auch ungewöhnlichen Anforderungen gerecht werden kann, insbesondere wenn es im unteren ppb-Bereich arbeitet.
Hinweis: Die zu diesem Artikel gehörige PDF ist zum Download nur auf Englisch verfügbar.
Literatur
[1] International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceutical for Human Use (ICH), ICH Q2(R2) Guideline: Validation of Analytical Procedures, 2023. Available at:
[2] DIN Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V., DIN 32645: Chemische Analytik – Nachweis-, Erfassungs- und Bestimmungsgrenze unter Wiederholbedingungen – Begriffe, Verfahren, Auswertung, 2008.
Verfügbar auf: https://www.beuth.de/

